All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Communicate these problems to relevant task teams, adhere to via till there's a remedy, and report the consumer resolution. Make certain that all tasks are following their spending plans and distribution times. Make a routine of tracking project turning points and dependences. Include these points in your normal records. Team up with other pertinent divisions, consisting of the item, sales, and support departments.
Establish a system to plan, track, and document every single program you manage. At least 4-6 years of experience in program administration with IT projects is important.
Innovation is the name of the video game when it comes to the innovation market, and within that standard, there's a behind-the-scenes orchestrator guaranteeing whatever runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Supervisor (TPM). This unhonored hero plays a critical duty in the success of technology projects, bringing order to turmoil and ensuring that the gears of growth turn efficiently.
What are the best Tpm Career Growth interview preparation tips?
It's a delicate dance in between setting ambitious objectives and ensuring assumptions continue to be securely based in truth - how to become a tpm. technical program manager jobs. Yet it's not almost producing a plan; it has to do with executing it perfectly. TPMs use the hats of both visionary coordinators and practical executors, making sure that every step aligns with the overarching project goals
In the large landscape of tech jobs, effective interaction is the bridge that attaches diverse groups and stakeholders. Below, TPMs shine as experienced translators, translating the intricate language of technology for non-technical stakeholders. They bridge the gap, making certain that everybody, no matter their technological background, understands the project's goals and progress.
They have the foresight to identify potential risks, varying from unexpected technological challenges to external aspects past the team's control. TPMs develop methods to reduce threats, guaranteeing that the project cruises with rainy weather with resilience.
Here, TPMs take on the role of allocators-in-chief, tactically dispersing resources to maximize performance. As the project landscape shifts, TPMs reapportion resources dynamically, ensuring that the group stays nimble and receptive.
What should I know before applying for a Technical Program Manager Courses job?
TPMs, in this regard, become the gatekeepers of quality. They established stringent standards for every component of the task, from code to layout, ensuring that the end item meets or exceeds the defined criteria.
TPMs develop a culture where excellence is not just an objective however a habit, permeating every element of the task. With their precise oversight, they infuse self-confidence in stakeholders and add to the long-term success and track record of the company. Being an effective TPM calls for greater than simply a knack for task monitoring.
Who offers the best Microsoft Technical Program Manager Interview certification?
While TPMs may not be coding wizards, they need a solid understanding of the technical landscape. This includes experience with the modern technologies entailed, a recognition of market fads, and the capability to understand the implications of technological choices.
In the technology globe, troubles are not obstructions yet challenges waiting to be solved. TPMs need a propensity for innovative analytical, thinking on their feet, and adjusting to unanticipated challenges. TPMs are the interaction nexus of a project. Whether it's communicating intricate technological information to a non-technical target market or promoting collaboration among team participants, reliable communication is non-negotiable.
Strategic believing includes anticipating obstacles, visualizing the project's trajectory, and straightening it with broader organizational objectives. As innovation progresses, so does the duty of the TPM. In recent times, the landscape has seen a change in emphasis from standard project management to a much more dynamic and flexible method. Agile has actually ended up being much more than simply a buzzword; it's a method of life for many TPMs.
, has come to be a keystone in the TPM's toolkit. In the age of large data, TPMs are increasingly relying on data-driven understandings to notify their decision-making processes.
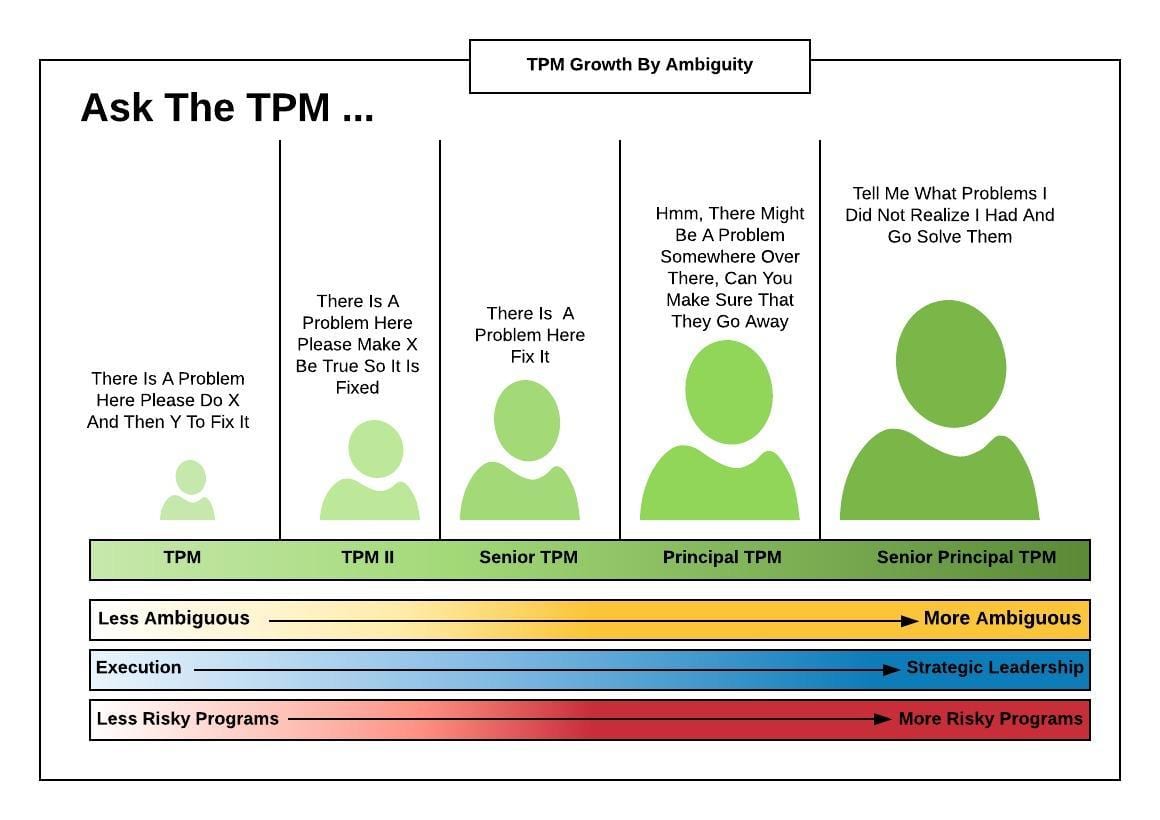
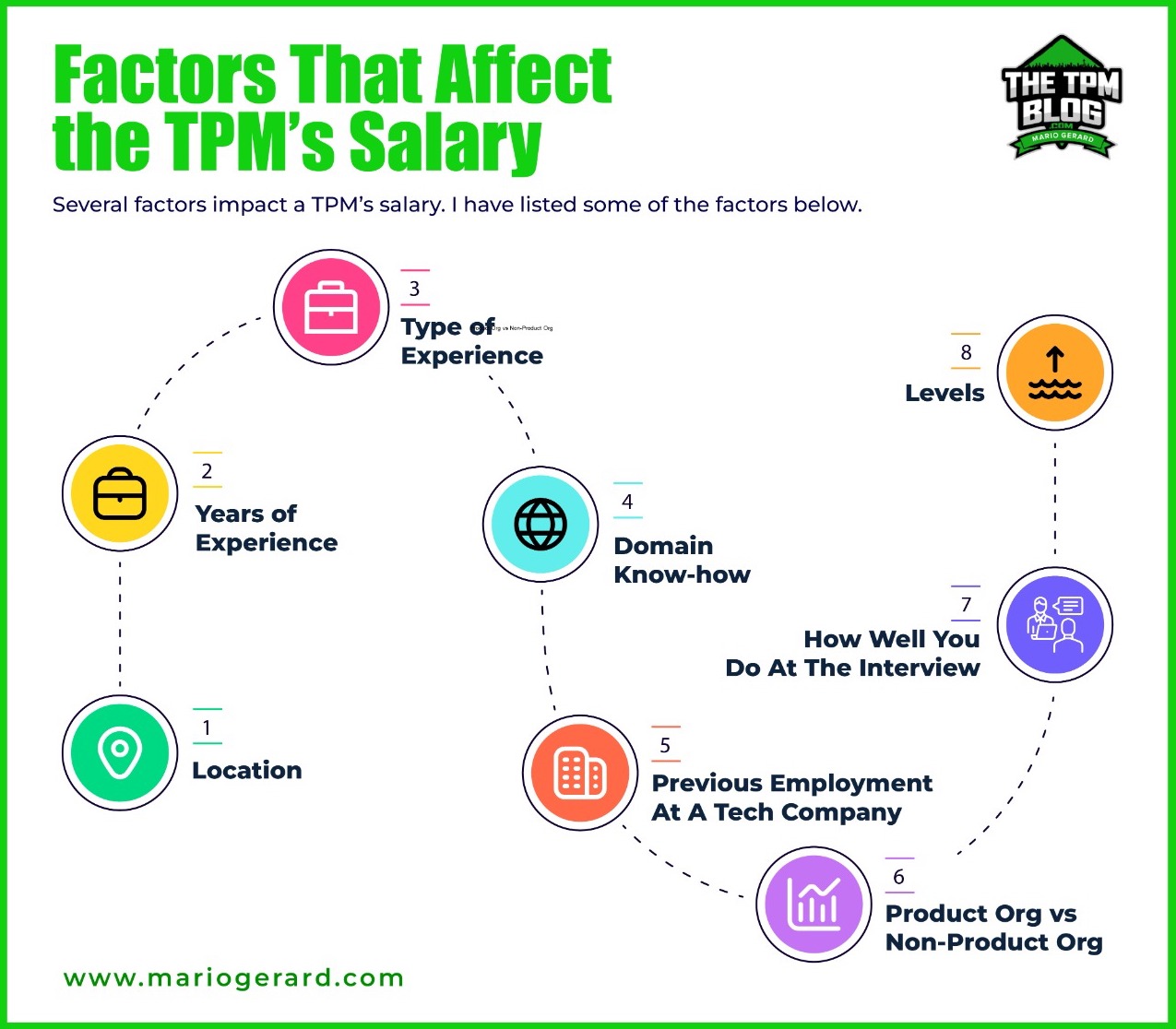
Tpm Salary Expectations

Unlike traditional project supervisors, TPMs must deeply recognize the technical elements of the jobs they manage. This double expertise allows them to communicate with engineering groups effectively, comprehend technological difficulties, and guarantee that projects are completed in a timely manner and within spending plan. Whether you're looking to work with a TPM or end up being one, recognizing the obligations and skill collections needed is essential for success in the tech industry.
The training courses cover important topics such as job lifecycle administration, danger analysis, source allocation, and software growth processes. With a focus on real-world applications, our training guarantees you are prepared to manage the intricacies of technical jobs in any type of industry. Gaining an accreditation can substantially enhance your job potential customers, showing to employers that you have the knowledge and abilities needed to prosper in a TPM duty.
From start-ups to Ton of money 500 business, companies throughout the world are seeking qualified professionals to lead their technological programs. Whether you're aiming to work with a TPM or are interested in TPM jobs, TPM Institute can help you navigate the job market and connect you with the ideal possibilities. Our courses are not almost learning; they have to do with releasing your career in one of one of the most popular areas in the technology market.
Our are dedicated to providing you with the most effective possible education and learning, offering insights grounded in real-world experience. They are devoted to assisting you accomplish your qualification and succeed in your job. For additional information regarding our programs and accreditations, at Take the following action in your job with TPM Institute and become a leader in technological program administration.
Tpm Skills For Tech Companies
There's a tendency for people to be attracted towards extremes when conceiving technical program supervisors. For circumstances, they're commonly called either always taking part in coding or not whatsoever. The fact exists is a range of technological deepness amongst TPMs, and this often differs by job and client. Some tasks call for a leader with simply enough technical depth to comprehend technology architecture and trade-offs.
They can verbalize intricate technical ideas to non-technical stakeholders and facilitate partnership in between diverse teams. TPMs excel at recognizing and solving issues that arise throughout job implementation, ensuring that jobs remain on schedule and within budget plan. They motivate and assist their teams, fostering collaboration, technology, and continual enhancement. TPMs' obligations can differ depending on the organization and the certain project they're servicing.
TPMs function to ensure that all group members are working in the direction of the very same goals, preventing miscommunication and squandered effort. TPMs proactively resolve possible problems, minimizing the chance of task delays and failings.
TPMs function to ensure that all team participants are working towards the very same goals, protecting against miscommunication and thrown away initiative. They anticipate and adjust to modifications in project demands, ensuring that jobs can pivot efficiently when required. TPMs proactively deal with prospective problems, lowering the likelihood of project delays and failures. They urge their teams to try out originalities and modern technologies, driving continual improvement and growth.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
How To Fast-track Your Faang Interview Preparation
How To Make A Standout Faang Software Engineer Portfolio
A Non-overwhelming List Of Resources To Use For Software Engineering Interview Prep
More
Latest Posts
How To Fast-track Your Faang Interview Preparation
How To Make A Standout Faang Software Engineer Portfolio
A Non-overwhelming List Of Resources To Use For Software Engineering Interview Prep